|
Glossary
CHAPTER 1. CLIMATE, TERRITORY AND POPULATION
Ageing index
The number of persons 60 years old or over per
hundred persons under age 15.
Catastrophic Occurrences, Losses and Relief
The Department of Disaster Management provides
relief assistance in cash or/and in kind to those who suffered
from natural and manmade disasters such as fire, floods, cyclone,
earthquake, thunderstorm, landslide, conflict and others.
The provision of assistance is based on the amount destructions
which are confirmed by the local administrative authorities
or/and regional the Department of Disaster Management.
Causes of Fire and Losses
Fire Services Department reports every month on its activities
to the Ministry of Home Affairs for information and extension
of relief to the victims.
Child Dependency Ratio
The ratio of child population (people younger
than 15 years) to the productive-age population(aged 15-64).
Dependency ratio
The number of dependent population per 100
working-age population.
District
States and Regions are divided into districts,
which in turn are subdivided into townships then towns, wards
and villages.
Foreigners residing
A person who is not a citizen of Myanmar
in which he or she is residing or temporarily staying.
Mean Maximum Temperature
The average daily maximum air temperature,
for each month and as an annual statistics, calculated over
all years of record.
Mean Minimum Temperature
The long-term average daily minimum air temperature
observed during a calendar month and over the year.
Mean Relative Humidity Percent
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air.
Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current
absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest point) for
that temperature.
Mean Temperature
The average daily maximum and maximum air temperature, for
each month and as an annual statistics, calculated over all years
of record.
Monthly Mean Temperature
The average of the mean monthly maximum and
minimum temperatures.
Old Age Dependency Ratio
People aged above 65 years as a share of
working-age population (aged 15-64). Data are shown as the
proportion of dependents per 100 working-age population.
Population density
The Population density relates to the number
of person in a give administrative area to the surface of
the area, expressed in square kilometers (km2).
Rainfall
The amount of water falling in rain, snow,
etc., within a given time and area, usually expressed as a
hypothetical depth of coverage.
Region
It is a specific area defined by having its
own characteristics.
Relative Humidity Percent
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in
the air. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures
the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum (highest
point) for that temperature.
Rural Area
Areas classified by the General Administration
Department as village tracts. Generally they are areas with
low population density and a land use which is predominantly
agricultural.
State
The territory occupied by one of the constituent
administrative districts of nation.
Total Dependency Ratio
A measure of the portion of a population
which is composed of dependents (people who are too young
or too old to work). It's equal to the number of people aged
below 15 or above 64 divided by the number of individuals
aged 15 to 64, expressed as a percentage. It is the sum of
the youth dependency ratio and the old-age dependency ratio.
Total Population
It is based on the de facto definition of
population, which counts all persons who were within the borders
of Myanmar on the night of 29th March 2014 (Census Night).
All Myanmar people working in its embassies abroad and their
families were counted in the census. The estimates of people
who were not enumerated in a few areas in Shan State, Kachin
State and Kayin State in the census.
Town
An urban area with a fixed boundary that
is smaller than a city or any more urbanized center than the
place of reference.
Township
An administrative division of a country.
Urban Area
Areas classified by the General Administration
Department as wards. Generally these areas have an increased
density of building structures, population and better infrastructural
development.
Village
The region where the boundary is stipulated
and formed under the Ward or Village Tract Administration
Law which is not included in the estate within the relevant
town boundary.
Village Tract
It is a group of adjacent villages.
Ward
A division or district of a city or town,
as for administrative or political purposes.
CHAPTER 2. HEALTH
AND SOCIAL WELFARE
Certified Veterinarian
A person who has been certified and is employed
by a licensed veterinarian.
Child Malnourishment: NCHS and WHO Standards
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO)
introduced new child growth standards for use in deriving
indicators of nutritional status, such as stunting, wasting
and underweight. These standards are based on the growth of
infants from six different regions of the world who were fed
according to WHO and United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
feeding recommendations, had a non-smoking mother, had access
to primary health care and did not have any serious constraints
on health during infancy or early childhood 3-6. It is recommended
that these new growth standards replace the previously recommended
international growth reference devised by the National Center
for Health Statistics (NCHS) in the United States. The prevalence
of malnutrition estimated using WHO standards is expected
to differ from that based on the NCHS growth reference because
there are differences in median weight-for-age, height-for-age
and weight-for-height between the two.(http://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/88/1/08-057901/en/)
Development of Border Area and National Races
Progress of Border Areas and National Races Department
to carry out development program in the border areas- 21 regions.
They are (1) Kachin state (2) Kayah state (3) Kayin state (4)
Chin state (5) Mon state (6) Rakhine state (7) Shan state (8)
Pa-O self Administered Zone (9) Palaung self Administered Zone
(10) Danu self Administered Zone (11) Kokaung self Administered
Zone (12) Wa self Administered Zone (13) Sagaing region (14) Naga
self Administered Zone (15) Taninthayi region (16) Bago region
(17) Yangon region (18) Ayeyawady region (19) Mandalay region
(20) Magway region and (21) Naypyitaw.
Fatality Rate
Ratio of deaths in an area to the population
of that area; expressed per 1,000, per year.
Health Structures
They are articulated in General and Specialist
Hospitals, Dispensaries, Health Centers by State, Region and Township
level.
Indigenous Medical Practitioner
A person whose primary employment role is to
diagnose physical and mental illnesses, disorders and injuries.
He prescribes medications and treatments based on the theories,
beliefs, and experiences indigenous of traditional medicine that
promote or restore good health.
International Classification of Diseases
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is the standard
diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical
purposes. It includes the analysis of the general health situation
of population groups. It is used to monitor the incidence and
prevalence of diseases and other health problems, proving a picture
of the general health situation of countries and populations.
All Member States use the ICD, which has been translated into
43 languages. Most countries (117) use the system to report mortality
data, a primary indicator of health status. ICD-10 was endorsed
by the Forty-third World Health Assembly in May 1990 and came
into use in WHO Member States as from 1994. ICD is currently under
revision, through an ongoing Revision Process, and the release
date for ICD-11 is 2018. http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/
Immunization, measles (% of children ages 12-23 months)
Child immunization measures the percentage
of children aged 12-23 months who received vaccinations before
12 months or at any time before the survey. A child is considered
adequately immunized against measles after receiving one dose
of vaccine. (http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/en/)
Iodized Salt Consumption Rate
Consumption of iodized salt refers to the
percentage of households who use edible salt fortified with
iodine.
Lady Health Visitor
She is a qualified nurse or midwife with post-registration
experience who has undertaken further training and education in
child health.
Public Health Supervisor
It is a highly responsible leadership and
supervisory position within the Department of Public Health.
Social Welfare Establishment
The schools and centers run by the Department
of Social Welfare provide various types of welfare services
to those who are received in respective institutions. The
Government establishes Women's Development Centers and Vocational
Training Centers for Women to provide institutional care,
health care, counseling, vocational training through income
generation activities and teaching of 3Rs. In the training
schools for boys and girls, orphans and abandoned ones are
accepted. Some boys and girls aged over 5 years are handed
from Residential Nurseries and some ones are admitted under
the Child Law (1993). Children are given care, social support,
formal education and vocational training. The Government also
takes responsibility to rehabilitate the persons with disabilities.
In the Vocational Training School for Adult person with disabilities,
vocational trainings such as silk screen-printing, photography,
TV repairing, computer training, carpentry and hair dressing
are provided. The School for Children with diabilities accepted
children of various types of disabilities such as amputees,
children with Down's Syndrome, Paraplegic and children who
are mentally retarded as well. Social Welfare services are
implemented not only by Government but also by NGOs establishing
schools and homes. Government provides grants-in-aids to those
NGOs with rice, funds for food, clothes and salary of the
administrators of the schools/homes every year according to
the rules and regulations. Voluntary pre-primary schools are
also provided with cash and technical assistance.
Social Protection Programs have been prioritized
and implemented step by step for most vulnerable groups to
protect and prevent from socio-economic risks and shocks as
well as to promote for their well-being.
Volume of Government Insurance Business
Data are referred to the number of insurance
policy, the amount of insured value and premium, the paid
claims of main insurances written by the state-owned Myanmar
Insurance. The Government started life insurance business
on 1st January 1957, and all other insurances business, such
as fire, marine, accidents, etc., on 1st October 1961. With
a view to safe guarding the interest of general public, the
Government introduced third party insurance scheme on 6th
July, 1976. Formerly "Air Travel Insurance" was shown in a
separate column. Now, it is incorporated under the "Miscellaneous"
column since its role is getting smaller. WHO Steps chronic
disease risk factor surveillance, Myanmar Steps Survey.
It was carried out Step 1 and Step 2 in Myanmar
from March 2009 to October 2010 by Department of Health. Socio
demographic and behavioral information were collected in Step
1. Physical measurements such as height, weight and blood
pressure were collected in Step 2. The STEPS survey, Myanmar
2009, was a population-based survey of respondents aged 15-64
years.
CHAPTER 3. VITAL STATISTICS
Age-Specific Fertility Rate (ASFR)
The age-specific fertility rate measures
the annual number of births to women of a specified age or
age group per 1,000 women in that age group. Unless otherwise
specified, the reference period for the age-specific fertility
rates is the calendar year.
Age Specific Mortality Rate (ASMR)
The age-specific mortality rate (ASMR), also called the age-specific
death rate, for a given population, a given age, and a given year,
refers to the number of deaths in that year to people of that
age for every 1000 people of that age.
Cause-Specific Death Rate
Cause-specific death rate is the number of deaths from a specified cause per 100,000 person-years at risk. The numerator is typically restricted to resident deaths in a specific geographic area.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births occurring in a
population during a given period of time, usually a calendar
year, i.e., the number of live births occurring among the
population of given geographical area during a given year,
per 1,000 mid-year total population of that area during the
same year.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths occurring in a population
during a given period of time, usually a calendar year, i.e.,
the number of deaths occurring among the population of given
geographical area during a given year, per 1,000 mid-year
total population of that area during the same year.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The number of infant deaths occurring during
the same period of time, usually a calendar year, i.e., the
number of deaths of live-born children under 1 year of age
occurring in a given geographical area during a given year,
per 1,000 live births occurring among the population of that
area during the same year.
Life Expectancy at birth
Life expectancy at birth is defined as the
average number of years that a newborn could expect to live
if he or she were to pass through life subject to the age-specific
mortality rates of a given period.
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) is the
ratio of the number of maternal deaths during a given time
period per 100,000 live births during the same time-period.
A maternal death refers to a female death from any cause related
to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management (excluding
accidental or incidental causes) during pregnancy and childbirth
or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective
of the duration and site of the pregnancy.
Natural Increase Rate
The rate of natural increase refers to the
difference between the number of live births and the number
of deaths occurring in a year, divided by the mid-year population
of that year, multiplied by a factor (usually 1,000). It is
equal to the difference between the crude birth rate and the
crude death rate.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
Total fertility rate (TFR) in simple terms
refers to total number of children born or likely to be born
to a woman in her life time if she were subject to the prevailing
rate of age-specific fertility in the population.
Under Five Mortality Rate (U5MR)
The under-five mortality rate is the probability
(expressed as a rate per 1,000 live births) of a child born
in a specified year dying before reaching the age of five
if subject to current age-specific mortality rates.
CHAPTER 4. JUSTICE AND SECURITY
Crime
Offense for which the main penalty of imprisonment,
fine and some accessory penalties ( i.e. interdiction from
Public Offices ) are provided.
Prisoners
People sentenced under measures restricting
freedom, held in prison in pre-trial detention or serving
a sentence.
Traffic Accidents
The Vienna Convention of 1968 defines the
accident as the fact that occurred in streets or squares open
to traffic where vehicles( or animals ) are involved still
or moving , and from which they are derived injury. They exclude
traffic accidents with only property damage.
CHAPTER 5. EDUCATION
B.Ed Correspondence Course of the Education of the University
of Education
Correspondence course in education is given
to in-service graduate teachers by the University of Education.
Enrollment in Arts, Science, Law and Economics is accepted
in the Yangon University of Correspondence Education (which
was established on 1967-1968 academic year) and Sagaing University
of Education (which was opened in 2000-2001 academic year).
The University was formerly called B.Ed Correspondence Section.
Monastic Education
With the aim of providing the needy children
and various parts of the country with education and enabling
them to become culturally refined citizen, 1,557 Monastic
Education Schools have been opened in 248 townships, attended
by a total of 26,074 novices, 15,486 nuns, 137,634 boy-students
and 129,775 girl-students in the 2017-2018 academic year.
Donations for Monastic Education are offered not only by people
within the country but also by people from abroad.
Pupil Teacher ratio
The average number of pupils (students) per
teacher as a specific level of education (primary, middle,
high) in a given academic year.
The School System
It is divided into three levels: primary, middle,
high. Data on Schools,Teachers and Students are presented by
Level, States and Regions.
The new system of Matriculation Examination
was introduced in 2001-2002 academic year in order to enable
students to study their preferred subject combinations. Students
are provided extensive and in-depth instruction of individual
subjects and taught at International Level. They are required
to take Myanmar, English and Mathematics as compulsory subjects
and a combination of 3 subjects- Physics, Chemistry, Biology,
Geography, History, Economics and Optional Myanmar - Constituting
and 8 subjects combination at the level of Basic Education
High School as follows;
(1)Economics, Physics and Chemistry
(2)Geography, History and Economics
(3)Geography, History and Optional Myanmar
(4)History, Economics and Optional Myanmar
(5)History, Physics and Chemistry
(6)Optional Myanmar, Physics and Chemistry
(7)Physics, Chemistry and Biology
(8)Geography, Physics and Chemistry
The University System
It is divided into Professional Institutes,
Universities and Degree Colleges. Classes at the institutes
of higher learning were suspended during 1989 and 1990 and
reopened in 1991. No examinations were held from 1988 to 1990.
Dagon University and the National University of Arts and Culture,
Yangon and Mandalay were opened in 1993. University of Computer
Studies (Yangon)was opened in 1987, Mandalay was opened in
1997 and Other Computer Colleges were upgraded as Computer
Universities on 20th January 2007. The International Theravada
Buddhist Missionary University was opened in 1998. Institute
of Medicine (Magway), University of Kyaukse and West Yangon
were opened in 2001. Meiktila, Hinthada Degree Colleges were
upgraded to University in 2001. Myanmar Aerospace and Engineering
University was opened in 2002.
Myanmar Maritime University (MMU) was established
in 1st August 2002 by the military government per the Myanmar
Maritime University Act (The State Peace and Development Council
Law No.1/2002). It is the premier university of maritime education
in Myanmar. MMU, administered by the Ministry of Transportation,
offers five-year bachelor's degree programs and two-year post-graduate
diplomas in various marine and naval disciplines. However,
Myanmar Maritime University changed to six-year Bachelors
degree programs except Nautical Science in 2012-2013 academic
year. MMU is one of the most selective universities in Myanmar
as MMU is to produce well competent qualified naval architects,
marine engineers and scientists. Admissions are based primarily
on the marks received in the university entrance examinations. Mingyan,
Moehnyin Degree Colleges were opened in 2003. West Yangon
Technological University (WYTU) was opened in 2005. University
of Public Health, Yangon was opened in 2007. Sagaing University,
Taung Goke and Mandalar Colleges were opened in 2012. Harkha
Degree College was opened in 2016-2017.
Vocational Trainees
A.G.T.I 3 Year course were commenced in 2013-2014
Academic Year at the Government Technical Colleges and Government
Technical institute under the Department of Technical and
Vocational Education and Training. The number of students
who attended the Bachelor of Engineering Courses at the Government
Technical Institutes and Government Technical Colleges under
DTVET shows Table (5.13).
CHAPTER 6. HOUSEHOLDS AND SOCIAL ISSUES
Housing Characteristics
In HIES (2001, 2006, 2012) and MLCS (2017),
information on ownership, tenure of dwelling and main used
of fuel for cooking. In MLCS 2017, information on different
type of walls, floors and roofs, type of lighting, good sources
of water by dry season and rainy season were collected by
using the questionnaire on housing characteristics.This section
will discuss the results obtained on ownership and type of
dwelling, lighting used and access to sources of water in
each dwelling.
National Library Statistics
The function of the National Library is to
supply documents and papers required by Government Agencies
and also to supply other materials required by the students
of Higher Education for references for their term papers.
From 1984 onward, the library is opening to the public.
Published books
All private books published according the
Printers and Publishers Registration Law 1962. Printers and
publishers are required to register under for their work.
They have also to submit regular information on books, magazines
etc. published, to Press Scrutiny and Registration Office.
Seizure of Narcotic Drugs
All Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances
seized according Law on 27th January 1993.The Law calls for
control of precursor chemicals and psychotropic substances
and money laundering, associated with illicit trafficking
of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
Video Services
All Videos produced, editing, filming, production,
duplicated, distributed, exhibited and rented and karaoke
according the Myanma Television and Video Act, which was laid
down in 1985 according to the PyithuHluttaw Act, Act No.12,
amended in 1996.
CHAPTER 7. LABOUR AND EMPLOYMENT
Employment to Population Ratio
The proportion of an economy's working-age
population that is employed. It provides information on the
ability of an economy to create jobs.
Employment through Labour Office
Job-seekers who are registered at Township
Labour Offices(16 Labour Offices in Yangon and 64 in different
States and Regions).
Labour force
Persons who are either in employment or in
unemployment as defined above constitute labour force. The
sum of persons in employment and unemployment equals the labour
force.
Labour Force Participation Rate
The proportion of the population ages 10
and older that is economically active, namely all people who
supply labour for the production of goods and services during
a specified period.
Overseas persons employed
Workers placed in overseas employment by
the Department of Labour, which provides services (through
overseas employment licensed agencies) signing MoUs and Bi-lateral
agreements with labour receiving countries.
Employment
Persons in employment are defined as all those
of working age who, during a reference period of seven days, were
engaged in any activity to produce goods or provide services for
pay of profit.
They comprise:
Employed persons "at work", i.e. who worked in a job for at least one hour;
Employed persons "not
at work" due to temporary absence from a job, or to working-time
arrangements (such as shift work, flexitime and compensatory leave
for overtime).
Unemployment
Persons in unemployment are defined as all
those of working age who were not in employment, carried out
activities to seek employment during a specified recent period
and were currently availiable to take up employment given
a job opportunity.
Outside labour force
Persons outside labour force are those of
working age who were neither in employment nor in unemployment
in the short reference period.
Labour underutilization
It refers to mismatches between labour supply
and demand, which translate in to an unmet need for employment
among the population. Measures of labour underutilization
include, but may not be restricted to:
(a)time-related underemployment,when the working time of persons in employment is insufficient
in relation to alternative employment situations in which
they are willing and available to engage;
(b)unemployment, reflecting
an active job search by persons not in emplyment who are available
for this form of work;
(c)potential labour force,referring to
persons not in employment who express an interest in this
form of work but for whom existing conditions limit their
active job search and/or their availability.
Social Security Scheme
Security Scheme was introduced in Myanmar
by Social Security Act, 1954 which came into enforce on 1st
January 1956. Now, to be in line with the international standard,
Social Security Law, 2012, was enacted and has been implemented
on 1st April 2014.
According to Social Security Law, 2012. By
Social Security Board which the following systems have been
operating the three insurance systems among the six insurance
systems:
(a)Health and Social Care Insurance System
(If the insured person is within 60 years of age at the time
of initial registration, 2% by the employer and 2% by the
worker, totally contribution for 4% and if the insured person
is over 60 years of age at the time of initial registration,
2.5 percent by the employer and 2.5 percent by the worker,
totally contribution for 5%.)
(b)Family Assistance Insurance System (Not
need to pay contribution)
(c)Employment Injury Insurance System (Only
the employer shall be pay contribution for 1 %.)
By the insured
workers have paid contribution under Social Security Law,
2012, who shall entitled to medical treatment in time of sickness,
confinement and employment injury at the establishment for
any cause and although the following cash benefits are entitled:
(a)Sickness Benefit of insured person (has
the right to enjoy 60 percent of average wage of the previous
four months as cash benefit relation to sickness up to 26
weeks.)
(b)Maternity Benefit of female insured worker
(has the right to enjoy 70 percent of average wage of a year
as cash benefit relating to maternity up to 14 weeks and then
if it is the twin delivery which has the right to enjoy another
four weeks for the child care.)
(c)Maternity expense of the female insured
workers (has the right to enjoy 50 percent for single delivery,
75 percent for twin delivery and 100 percent for triplet delivery
and above of average wage of a month.)
(d)Miscarriage benefit of the female insured
(has the right to enjoy 70 percent of average wage of a year
as cash benefit relating to miscarriage up to 6 weeks.)
(e)Adoption the child under 1 year of the
female insured worker (has the right to enjoy 70 percent of
average wage of a year as cash benefit relating to adopt up
to 8 weeks.)
(f)Paternity Benefit of the male insured
(has the right to enjoy 70 percent of average wage of a year
and 15 days leave for infant care.)
(g)Maternity expense of the male insured
for paternity whose wife is an uninsured (has the right to
entitled half of maternity expense.)
(h)Medical treatment benefit for her child
on confinement of female insured (has the right to take medical
treatment for her child up to one year.)
(i)Funeral Expense (if the insured person
is deceased for any cause, for a person nominate or dependent
of those insured that they can be claimed to entitled up to
maximum of five times from one time for funeral expense.)
(j)Medical Treatment for Retired (insured
civil services after retiring who has the right to take the
continuously medical treatment if it had paid contribution
for 180 months and above under the combined of the Social
Security Law, 2012 and Social Security Act 1954.)
(k)Scholastic stipend for the children of
the insured couple earn less than the stipulated amount of
income (has the right to enjoy 10 percent of average wage
for a child living schools age of education years.)
(l)Family Assistance for natural disaster
of insured worker (has the right to entitled 40 percent of
average wage of a month.)
(m)Temporary Disability Benefit (has the
right to entitled 70 percent of average wage of a month for
reducing or ceasing of earning by reasons of incapable to
work of employment injury.)
(n)Permanent Disability Benefit (has the
right to entitled five years to nine years in lump sum with
calculation based on 70 percent of average wage of a month
of the partial capacity and total loss of capacity for work
due to employment injury.)
(o)Survivors Benefit for deceased of employment
injury (has the right to entitled 30 times up to 80 times based
on contribution of the insured person.)
CHAPTER 8. NATIONAL ACCOUNTS
Gross Domestic Product
The monetary value of all the finished goods
and services produced within a country's borders in a specific
time period. Though GDP is usually calculated on an annual
basis, it can be calculated on a quarterly basis as well.
GDP includes all private and public consumption, government
outlays, investments and exports minus imports that occur within
a defined territory. GDP is a broad measurement of a nation's
overall economic activity.
Per Capita GDP
The total output of a country that takes
the gross domestic product (GDP) divided by the number of
people in the country. The per capita GDP is especially useful
when comparing one country to another because it shows the
relative performance of the countries. A rise in per capita
GDP signals growth in the economy and tends to translate as
an increase in productivity.
Real Economic Growth Rate
A measure of economic growth from one period
to another expressed as a percentage and adjusted for inflation
(i.e. expressed in real as opposed to nominal terms).
CHAPTER 9. AGRICULTURE
Acre
It is equal to 0.4047 hectares.
Agriculture
Land are classified into reserved forests,
current fallows, net area sown, cultivable waste other than
fallows, other wood land and others.
Crops
They are classified into Sown(planted) acreage,
harvested acreage and production ton.
Ton
It is equal to 1.01604 metric ton.
CHAPTER 10. FORESTRY
Permanent forest estate
Permanent forest estate means forest area
that is designated by law or regulation to be retained as
forest and may not be converted to other land use. Permanent
Forest Estate includes three categories:
-Reserved Forest
-Protected Public Forest
-Protected Area System
Reserved forest and protected public forest
area
Reserved forest means land constituted as
a reserved forest under Myanmar Forest Law 1992.
Protected Public Forest
Protected Public Forest means land declared
to be protected public forest under Myanmar.
CHAPTER 11. INDUSTRY, CONSTRUCTION AND MYANMAR BUSINESS SURVEY
Persons Engaged in Metalliferrous Mines by Type of Mining
Underground workers are defined as those
workers who work in the tunnels under the ground. Open working workers
are defined as those workers are working below the surface
with open cuts.
Housing Development
The National Housing and Town and Country
Development Board which was formed in October 1951, was reorganized
and reconstituted into Housing Board at the end of 1965. In
March 1972, along with the general reorganization of all government
departments, the Housing Board became the Housing Corporation
and was later renamed as Housing Department. With effect from
1st July 1990, Housing Department was again renamed as Department
of Human Settlement and Housing Development. It was charged
with planning and execution of all residential housing schemes
undertaken by the State. But the responsibility for actual
construction work was entrusted to the Construction Corporation
which was renamed in April 1989 as Public Works. In 1988-89
the Department of Human Settlement and Housing Development
has introduced the Urban Development Housing Scheme under
which private contractors are permitted to construct buildings
of different designs in the vacant plots of the downtown areas
of the Yangon City, with their own monies. After completion
of the construction, family units in the buildings are divided
according to the ratio agreed upon, by the Department and
the contractors. With effect from 1st April 2015, Department
of Human Settlement and Housing Development, was reformed
as Department of Urban and Housing Development.
Private Buildings
Number of applications submitted to and approved
by the Yangon City Development Committee and construction
completed. They are classified into two categories viz., (a)
new buildings and (b) extension and repairs.
School Construction
Schools constructed by the Ministry of Construction and Private
contractors.
Bridges
The bridges statistics were compiled from
the Department of Bridge under the Ministry of Construction.
It do not include the bridges constructed by other departments.
Economic Activity of Business
Myanmar Business Survey-MBS(2015) covered the distribution
of businesses are more than One hundred and Twenty Six thousands
which are registered across various economic sectors. In the Manufacturing
sector, the vast majority of businesses are Manufactured food
products, beverages and tobacco products. Likewise, in the Services
sector, more than half of the businesses are engaged in food and
beverage service activities. Regarding to the distribution of
businesses by size, larger businesses with 50 or more workers
constitute only a tiny fraction of the overall economy. Mostly
the age of businesses are 20 years and above. The sectoral pattern
of substantial variation shows that there is a fairly even distribution
between Manufacturing, Trade and Service businesses, Mandalay,
Sagaing, Mon and Ayeyawady are more dominated by Manufacturing
firms while in Yangon. Moreover, Businesses are mostly registered
with Municipal Offices in the respective regions.
CHAPTER 12. TOURISM
Tourist
A person travelling to and staying in places
outside their usual environment for one purpose (United Nation
World Tourism Organization's).
CHAPTER 13. COASTAL TRADE
Coastal Trade
Coastal trade statistics are related to the out-shipment and
in-shipment of goods by sea-going vessels between Myanmar seaports.
Shipping bills have to be filled at the Customs Department if
goods are to be transported from one Myanmar seaport to another
one. When the goods arrive at the destination, a bill of entry
has to be filled if the goods are from Yangon; otherwise no bill
of entry is necessary. These shipping bills or bills of entry
forms are the basis of statistical information. The date of departure
or arrival of the ship is taken as the date on which the out-shipment
or in-shipment takes place.There are eleven seaports along Myanmar
coast but Pathein and Maungdaw are neither export nor import
to Yangon port.
In-shipment
In-shipment is shipping entry to Yangon seaport
from other seaports in Coastal.
Out-shipment
Out-shipment is shipping clearance from Yangon
seaport to other seaports in Coastal.
CHAPTER 14. FOREIGN TRADE AND INVESTMENT
Balance of Payments
A statistical statement for a given period
showing (a) transactions in goods, services and income between
an economy and the rest of the world; (b) changes of ownership
and other changes in that economy's monetary gold, Special
Drawing Rights (SDRs) and claims on and liabilities to the
rest of the world; (c) unrequited transfers and counterpart
entries that are needed to balance, in the accounting sense,
any entries for the foregoing transactions and changes which
are not mutually offsetting.
Coverage of Foreign Trade Statistics
Data include government and private exports
and imports on trade account, gifts, aids, and parcel posts.
Sale of goods, whether foreign or national to all foreign
trading ships are included in export statistics. All data
exclude exports and imports under military accounts. Exports
and imports under diplomatic privileges have been excluded
since 1966. Starting from November 1988, when border trade
was opened, the total foreign trade data include border trade.
Export declaration forms and import declaration
forms filled by the respective exporters and importers and
checked by customs officials constitute the major source of
information in compiling foreign trade statistics. Up to 2000-2001,
statistics on rice and rice products, timber, gem, marine
products and oil and gas are obtained from the Myanmar Agricultural
Produce Trading, Myanmar Timber Enterprise, Myanmar Gem Enterprise,
Union of Myanmar Economic Holdings Limited, Department of
Fishery and Myanmar Oil and Gas Enterprise respectively. Since
2001-2002, all exports and imports statistics are obtained
from the customs department.
Exports
Domestic exports are exports of national
products. All exports are domestic exports plus re-exports
from bond and other than from bond. Exports were formerly
recorded according to the date of shipment have; since November
1967, they are recorded according to the date of completion
of consignment.Exports are credited to the country of final
destination or of ultimate consumption. Exports are valued
at Free on Board (FOB), namely at port or place of dispatch
of exporting country (including export duties, internal taxes
and similar charges to the extent that they remain charged
on the goods and passed on to the importers).
Imports
They are the sum of goods released direct from Customs wharves
for domestic consumption (direct imports for consumption) and
goods passed to be bonded (imports into bond). Imports were formerly
recorded according to the date of payment of duty have; since
November 1967 they are recorded as of the date of arrival of goods.
Imports are credited to the country of primary origin or production.
Imports are valued at Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF), namely
at port or place of arrival of the country (excluding customs
duty and other import charges).
Import and Export Indices
Quantum Indices of exports and imports are
computed to gauge the changes in the quantity of external
trade when the effects on price movements are eliminated.
Unit value indices are designed to provide means of measuring
changes in the average unit value of commodities exported
or imported.
Trade Category-General import figures
and domestic export figures for certain selected commodities
are used in computing the indices and include trade under
private and government accounts.
Method - Both the Quantum and the
Price Indices are of the aggregative type computed with Laspeyre's
formula. The unit sale of each commodity is the CIF or FOB
per unit value of general imports and domestic exports respectively.
Base year are 1985-1986, 2000-2001,2005-2006 and 2010-2011.
Foreign Investment
Foreign investors can set up their business
either in the form of a wholly foreign-owned or a joint venture
with any partner (an individual, a private company, a cooperation
society or a state-owned enterprise). The maximum foreign
investment capital ratio shall not be more than eighty percent
of the total investment amount if the foreigner has formed
joint-venture with the citizen to carry out prohibited or
restricted business.
Myanmar Citizens Investment and Inducement
Myanmar Citizens Investor can set up their
business in the form of private company, public company and
joint venture with local companies according to the Myanmar
Citizens Investment Law (MCIL) enacted on 29thJuly 2013.
CHAPTER 15. TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATIONS
Transports
Railway Transport, Airways Transport, Road
Transport and Inland Water Transport.
Passenger-Mile
One passenger-mile corresponds to the transport
of one passenger over one mile.
Freight Ton-Mile
One ton-mile corresponds to the transport of one ton of freight
over one mile.
Railway Transport
Data represent the operation on all railway
lines in the country except railways serving plantation, forests,
mines or industrial plants. Statistics relating to diesel
locomotives do not include diesel rail cars.
Airways Transport
It includes public and private sectors for all
traffic, both revenue and non-revenue, performed by the Myanmar
International Airlines on scheduled services, non-scheduled services,
special and charter services. Data relating to cargo represent
the total freight, baggage and mail irrespective of whether the
freight is charged or not.
Road Transport
Passenger statistics include bus and taxi
services. Road statistics include Union arterial highways
and highways for Myanmar proper only. With the establishment
of the new administration in March 1972, data for the year
1972-73 and after, include road under States administration.
Inland Water Transport
Inland water transport statistics are related
to all traffic of powered vessels of the government functioning
on commercial lines.
Shipping Statistic
They exclude vessels on government duty including
military, pleasure craft and fishing vessels.
Communications Statistics
Statistics on perfomance of posts and telecommunications
services are obtained from the Posts and Telecommunications Department,
Myanmar Posts and Telecommunication (MPT) and Myanmar Posts, while
data on television relay stations are provided by Myanma Radio
and Television.
Cellular Mobile Telephone System was begun in
Yangon and Mandalay in 1993 and 1996. Global System for Mobile
Communication (GSM) has introduced in Yangon and Mandalay in 2003
and extended to other states and regions very soon.
MPT provides internet services to some government
agencies and private companies with an initial capacity of 400
dial-up lines since 1998. In 2014, the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications
allowed private sector inclusion in mobile phone and internet
services. At present, public service provider, MPT and private
service providers such as Telenor, Ooredoo, Mytel are providing
mobile telephone services and internet services in all over the
country. Internet and Mobile phone subscription has been dramatically
increasing since 2014. Now, mobile phone subscribers per 100 people
are 106 in Myanmar.
CHAPTER 16. PRICES AND INTERNAL TRADE
Retail Price
Retail price means the price of a good or product
when it is sold to the end user for consumption, not for resale
through a third-party distribution channel.
Average Retail Prices
Central Statistical Organization collects average retail prices
of commodity from the selected markets in the municipal area
of Yangon City as well as all other cities of (82) Townships.
Wholesale Price
The cost of a goods sold by a wholesaler.
Average Wholesale Prices
Wholesale prices are collected directly from the wholesale centers in Yangon by monthly.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the changes of goods
and services from household's expenditure that can effect
on the actual demand. Price index can reflect the average
changes of household's expenditure. Generally, index is a
unit and designated as a basis for a year, household's expenditure
is equal 100 in the base year. After that, the changes of
goods and services are calculated using base year by monthly
and year for showing ratio or percentage. A measure of the
overall level of prices shows the cost of a fixed basket of
consumer goods relative to the cost of the same basket in
a base year.
The 2012 base year computes CPI by using the
following Modified Laspeyres's Price Index formula:

Commodity Basket
Commodity basket also called basket of goods. A collection
of products, raw materials and services which are comprised
the Consumer Price Index (CPI) over a period. The basket typically
indicates consumer buying behavior across a diverse set of
offerings.
The 2012 CPI introduces the UN COICOP classification.
The classification is used internationally possible to make
international comparison of inflation at more detailed levels.
The 2012 CPI basket has 274 products and services, 108 food
items, 166 non-food items including goods and services. There
are new 116 items in the index, for example new and used cars,
mobile phones and mobile phone charges and computers, etc.
2012 CPI based on only non-purchased items are excluded from
total expenditure.
Inflation
An increasing overall level
of prices is rising in the long period.
Inflation Rate
The percentage increase in the price of goods
and services, usually, annually. The inflation rate means
the average price of commodities has risen for a long period
of time, that situation refers total demand is higher than
total supply. In other words, the inflation rate shows climbing
price index.
When price rose, the value of money reduced which
has to use large sums of money to get needed amount, that
growing amount of money as inflation.
Year on Year Inflation
The Inflation can be measured by
computing percentage change in current month CPI from month
to month or percent change from the same month of the prior
year, according to the following formula:

Annual Rate of Inflation (or) Average
Rate of Inflation
The average rate of inflation is computed
monthly CPI growth rate within a year taking 12 month of year,
according to the following formula:

Gold Price Gold prices are collected from gold dealer by daily
for the highest, lowest, and the average prices of 24 carat
and 22 carat gold in Yangon.
Co-operative Statistics
Statistics on co-operative activities are provided by the Co-operative
Department. The major objective of co-operative society is
to procure, produce, and distribute essential goods and services
to the consumers through the respective co-operative societies.
Co-operative statistics shows the number of societies, number
of members paid-up share capital, bank loan, reserve fund,
other fund, liabilities, net profit, and working capital from
co-operative societies.
CHAPTER 17. PUBLIC FINANCE, BANKING AND FINANCIAL MARKETS
Public Finance
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar Budget has
been classified into the Union Budget and State and Region Budget
since 1stOctober 2011-2012.
Nay Pyi Taw Development Committee is drawn on the basis of
self-financing since 2006-2007.
Some of the state-owned Economic Enterprises under the Ministry
of Transport have been carried out their functions outside
the Union Fund and Yangon Electricity Supply Corporation since
2013-2014 and Mandalay Electricity Supply Corporation have
been carried out their functions with their own fund since
2015-2016.
Social Security has been carried ut their functions outside
the Union Fund except for services personal wages and salaries
since 2013-2014.
Central Bank of Myanmar is carried out its functions with
its own fund beginning from 2015-2016. When Central Bank makes
profit, it shall deposit 40% of net profit to General Reserve
Fund. But when Central Bank makes a loss, it shall set off
from General Reserve Fund.
Currency in Circulation (CIC)
The central bank's liability for currency in circulation
is equal to the total amount of currency issued by the central
bank less the central bank's own holding of national currency.

Currency Outside Depository Corporations
The currency outside depository corporations is equal to
the total amount of currency issued by the central bank less
currency holdings of depository corporations (central bank
and other depository corporations). It is also equal to the
amount of currency in circulation less currency holdings (vault
cash) of other depository corporations. 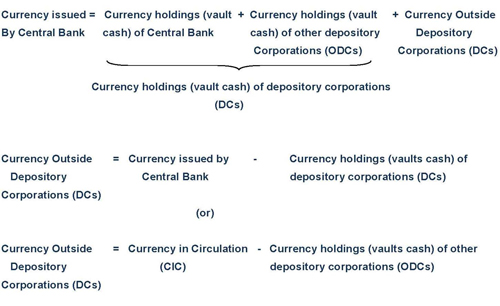
Transferable Deposits
Transferable deposits comprise all deposits that are exchangeable
on demand at par, without penalty or restriction, and that
are otherwise commonly used to directly make payment.
Money Supply
Money supply is the aggregates money within an economic system
in a given period.
Money supply is classified as M1, M2 and
M3, according to the type and size of the account in which
the instrument is kyat.
Money supply (M1) or narrow money consists of currency outside
depository corporations and transferable deposits.
M1 = currency outside depository corporations + Transferable
Deposits
Money supply (M2) or broad money covers M1 and other (or
nontransferable) deposits which include savings certificates,
saving deposits, time deposits and other types of deposits.
M2 = M1 + Other (or nontransferable) Deposits.
People's Savings
People's savings covers savings deposits, time deposits,
other deposits and savings certificates issued by Myanma Economic
Bank.
Savings deposits, time deposits, other deposits are accepted
by state owned banks as well as all private banks. Savings
certificates are issued by Myanmar Economic Bank under the
new Savings Bank Law 1992 and issued various types of denominations:
Kyat 5, Kyat 10, Kyat 50, Kyat 100, Kyat 500, Kyat 1000, Kyat
10,000, Kyat 100,000, Kyat 500,000 and Kyat 1,000,000 respectively.
The maturity period is twelve years from the date of issue.
At the option of the certificate holder, it may be redeemed
at any time after twelve months from the date of issue with
accrued interest for relevant period. The data is shown in
table 17.14.
Treasury Bonds
Two types of government treasury bonds, three-year treasury
bonds and five-year treasury bonds are issued with effect
from 1stDecember, 1993 with a view to giving an opportunity
of investment for the public and private enterprises. Moreover,
two-year treasury bonds are issued since 1stJanuary, 2010.
The data is shown in table 17.15.
Interest Rates
Central bank rate, interest on treasury bills and bonds,
deposit rates and lending rates are shown in table 17.16.
Central Bank Survey
Central Bank Survey in table 17.17 shows the compiled position
based on SRF-1SR which covers the Central Bank's balance sheet
source data.
In 2004, the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
introduced the Standardized Report Forms (SRF), a unified framework
for countries' reporting of monetary and financial statistics
to the IMF. The SRF allows for cross-country harmonization of
sources of data and methodology for the compilation and presentation
of statistics in a transparent and consistent manner.
SRF 1SR.
Include data for the central bank (the accounts
of the central bank headquarters and branches and, if applicable,
the currency board or independent currency authority that
issues domestic currency). If the monetary authorities' functions
are performed outside the central bank, these should be reported
as supplementary data. These include (1) official foreign
exchange holdings by the government, (2) currency issuance
by the government, and (3) transactions with the IMF performed
by the government.
SRF 2SR.
Include data on all resident units in the
Financial Corporations - FCs sector (except the central bank)
that issue liabilities included in broad money. "Offshore
banks" (that is, FCs that are designated as "offshore") that
issue liabilities included in broad money should be included
in the data in the SRF. The SRF include the accounts of nonoperating
Other Depository Corporations - ODCs that are being reorganized
or are in the process of being liquidated, even if the nonoperating
corporations' liabilities are excluded from broad money.
The ODC sector represents depository institutions, excluding
the central bank, that issue liabilities included in the national
definition of broad money. The institutional coverage of the
ODC sector varies per country, but at the broadest level may
include commercial banks, credit unions, savings institutions
and money market mutual funds.
Establishment of Domestic Private Banks
The Central Bank of Myanmar has granted the banking license
to domestic private banks since 1992. At the end of May 2016,
24 private banks were operating the banking services in the
country.
State Owned Banks' and Private Banks' Survey
State Owned Banks' and Private Banks' Survey in table 17.18
shows the positions based on SRF-2SR which covers the consolidated
balance sheets source data of Myanma Economic Bank, Myanma
Foreign Trade Bank, Myanma Investment and Commercial Bank,
Myanma Agricultural Development Bank and Private Banks.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
Foreign Exchange reserves in table 17.19 include gold and
foreign currencies. Previously, gold was valued at SDR 35
per fine troy ounce and converted into Kyat at the official
exchange rate of K 8.50847 per SDR. Since 1997, the value
of gold in the foreign exchange reserves has been based on
London Gold Market rate. Foreign currencies are valued at
the reference rates.
Broad Money Survey
Broad Money Survey in table 17.20 shows the monetary aggregates
positions based on the financial statements of the Central
Bank, and commercial banks both state-owned and private owned
banks in accordance with the MFS SRF-based compilation framework.
|